Langmuir Monolayer Project
X-ray Scattering and Optical Studies of Langmuir
Monolayers
Former Project Members:
The Langmuir monolayer work at Harvard is currently supported by
the National Science Foundation
through Grant No. NSF-DMR-98-72817.
Measurements at the NSLS are supported by DOE grant DE-AC02-76CH00016.
Investigators from other institutions that collaborate with us receive
other support.
Project summary:
Langmuir monolayers (LMs), i.e. one-molecule thick films at the gas/water
interface, provide one example of real physical systems which should
allow an experimental study of two-dimensional (2D) physics. The principal
goal of this project is to study the statistical and structural properties
of 2D phases formed by LMs by utilizing various surface-sensitive x-ray
scattering techniques.
Through the grazing incidence diffraction (GID) studies aided by high-intensity
synchrotron-generated x-rays, the microscopic structures of ordered LM
phases of simple surfactant molecules (e.g., fatty acids, fatty alcohols,
and phospholipids) were characterized in the late 80s through mid 90s
by different research groups, with our group being one of them.
These studies demonstrated that the long-chain amphiphilic molecules form
close packed 2D structures on water in which the chains are oriented either
normal to the surface or tilted at relatively small angles to the surface
normal. These structures are similar to the various tilted and untilted
phases of smectic liquid crystals.
Our more recent efforts are directed towards studies of LMs formed by larger
molecules, which are not necessarily amphiphilic like the aformentioned simple
surfactant molecules and are shaped either like a sphere or a rod. The larger
size of the molecules implies that the constructive interference in the GID
patterns that can be used to characterize intermolecular packing occurs at
smaller angles with larger amplitudes. The combination of this and the large
scattering power due to a greater number of electrons per molecule has the
important consequence that broad GID peaks may be observed from disordered
LM phases. This would make it possible to characterize the structural
changes in not only ordered but also noncrystalline part of 2D phase diagram.
One class of LM systems of current interest are sphere-like molecules,
consisting of derivatized gold nanoparticles which are "hairy" due to
the attachment of hydrocarbon chains around them. For these LMs, we
collaborate with Prof. R.B. Lennox and his group at McGill University.
The large number of electrons contained in the gold core provides a
high x-ray contranst that is advantageous for x-ray scattering studies.
The metal nanoparticle LMs are interesting also from a practical standpoint;
for example, the observation of a 2D metal/insulator transition has been
reported recently for LMs of silver nanoparticle coated with short thiol
chains.
Another class of LMs currently being studied consist of
a-helical poly(glutamates) which are synthetic
polypeptides with a rigid rod-like molecular shape. For this project, we
collaborate with Prof. D.A. Tirrell and his group at Caltech. Unlike the
conventional long-chain amphiphilic molecules, these rod-like molecules are
oriented parallel to the water surface. That is, their molecular axes lie
within the LM plane, just as in a 2D plane perpendicular to the helical axis
of a cholesteric liquid crystal.
Our recent work on these different LM systems include:
- Observation of liquid-like 2D structure factor from amorphous LMs.
- Characterization of first-order mono/bilayer transitions.
- Characterization of microscopic inhomogeneities within Langmuir films
via excess off-specular diffuse scattering.
Examples of studied systems:
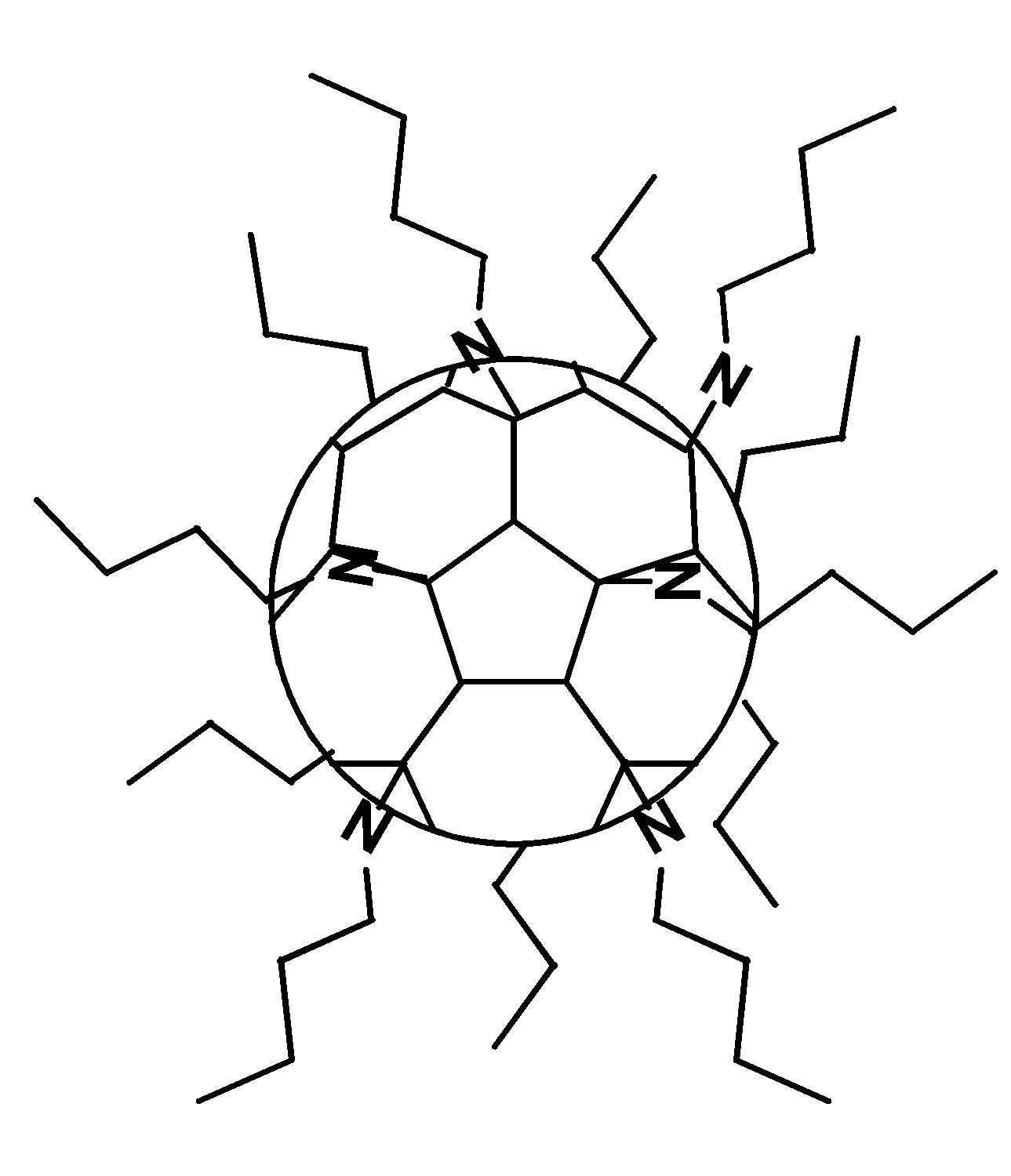
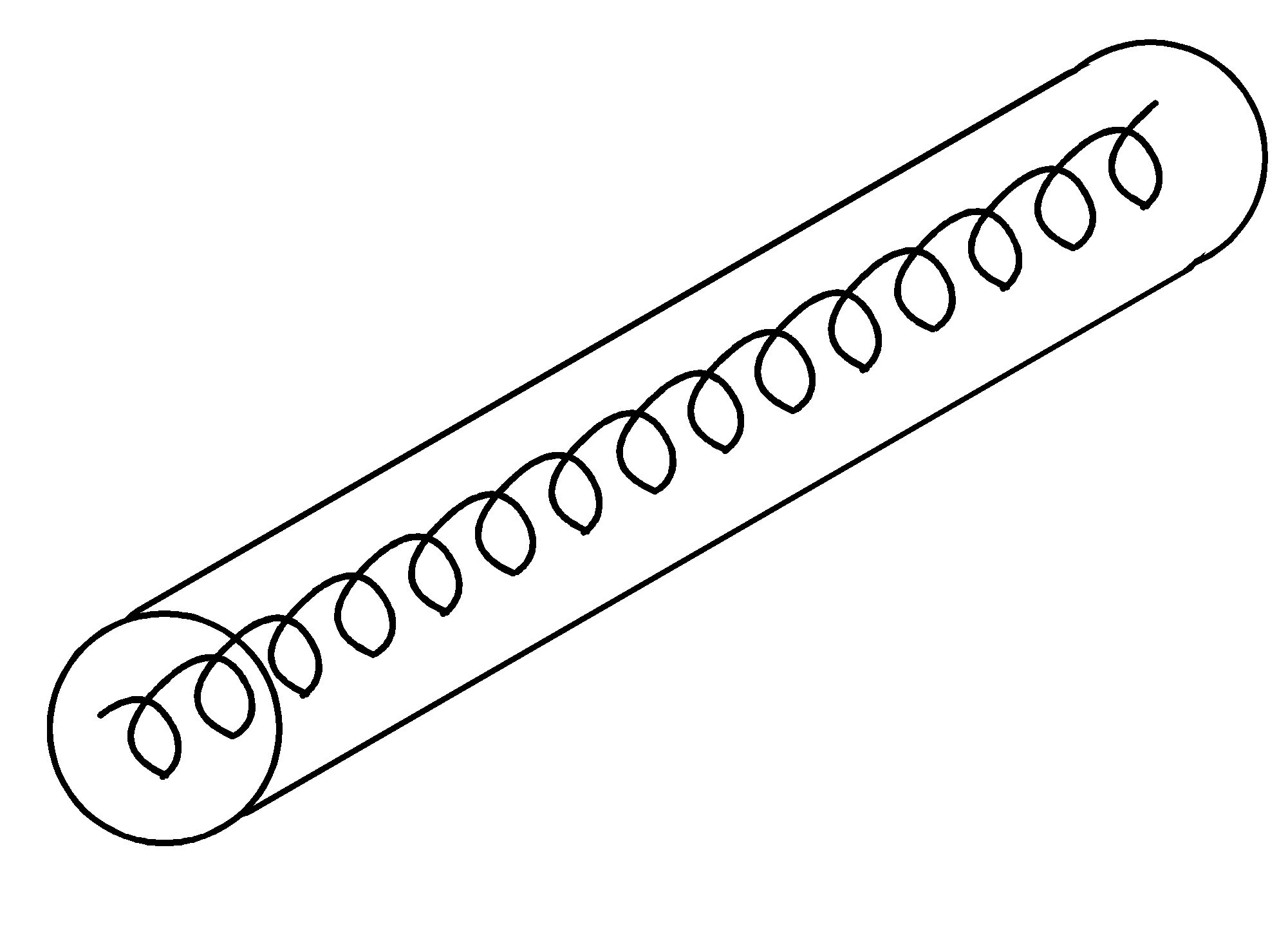
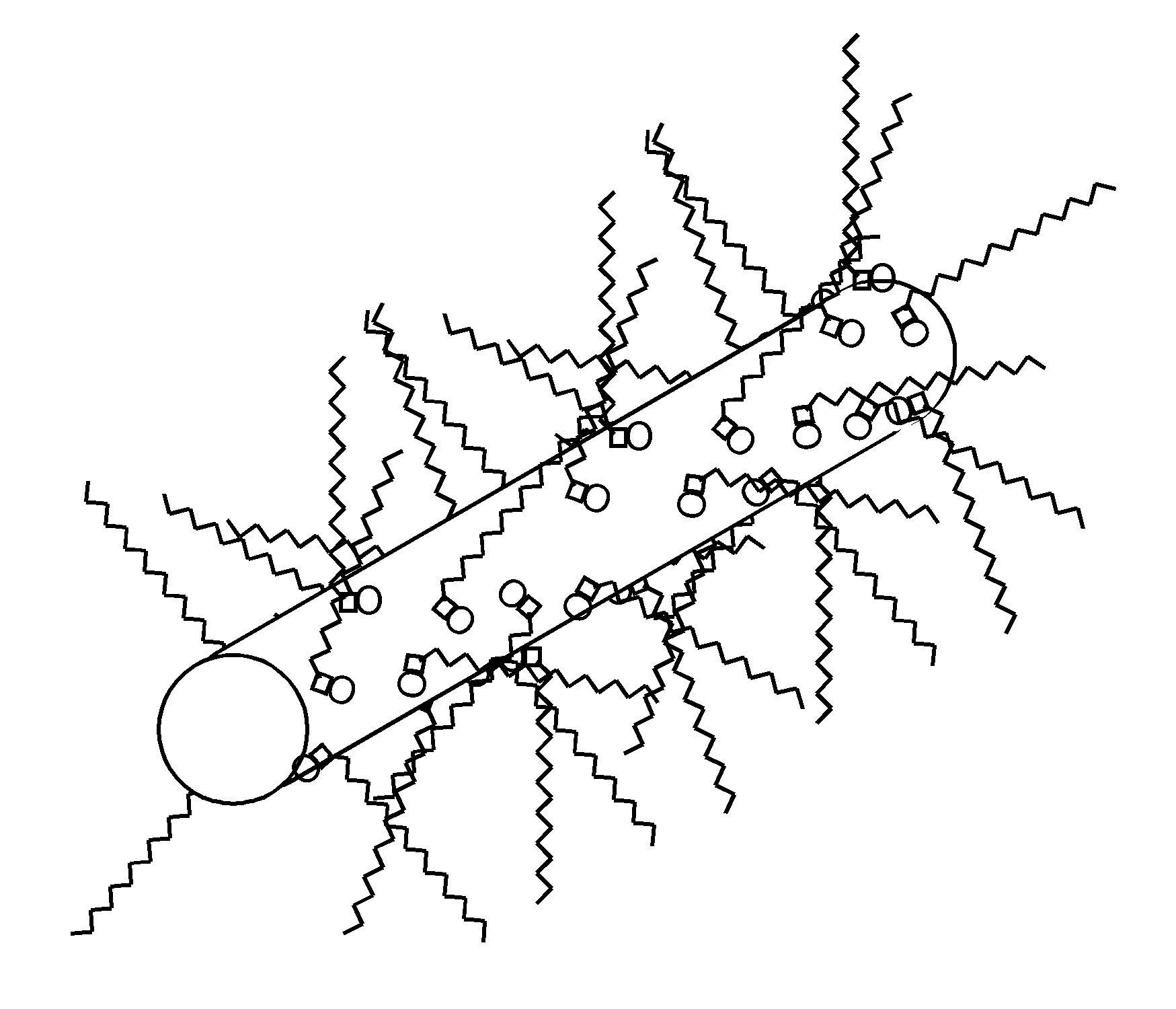
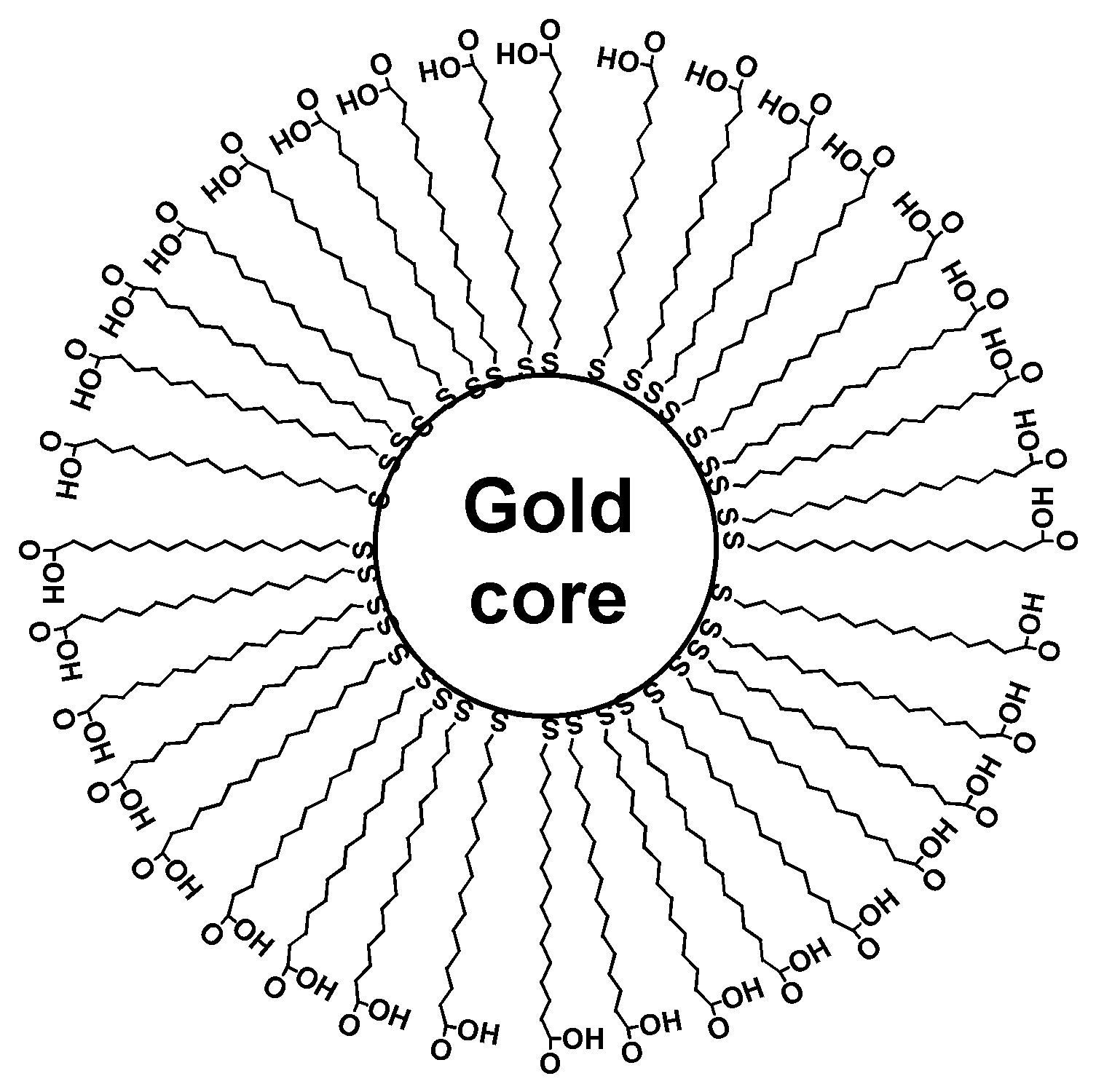
(1) C60-propylamine adduct monolayers (sphere-like)
In collaboration with Prof. David Vaknin of Ames Lab and Iowa State
University.
- J. Chem. Phys. 107, 5531 (1997). PDF
(2) PBLG (poly(g-benzyl L-glutamate)) monolayers
(rod like)
In collaboration with Prof. David A. Tirrell of Caltech.
- Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 3455 (1998). PDF
- J. Chem. Phys. 111, 9761 (1999). PDF
(3) C16-O-PBLG (poly(g-4-(hexadecyloxy)-benzyl L-glutamate)) monolayers ("hairy rod")
In collaboration with Prof. David A. Tirrell of Caltech.
- Phys. Rev. E 66, 010601(R) (2002). PDF
- J. Chem. Phys. 119, 6253 (2003). PDF
(4) Derivatized gold nanoparticle monolayers (sphere-like)
In collaboration with Prof. R. Bruce Lennox of McGill University.
- J. Chem. Phys. 120, 3446 (2004). PDF
Experimental techniques used:
- Surface pressure vs area/molecule isotherm
measurements, both relaxation and continuous methods.
- Brewster angle microscopy.
- X-ray specular reflectivity.
- Grazing incidence x-ray diffraction (GID).
- Off-specular x-ray diffuse scattering.
Related publications from our group:
- M. Fukuto, R.K. Heilmann, P.S. Pershan, A. Badia, and R.B. Lennox, "Monolayer/Bilayer Transition in Langmuir Films of Derivatized Gold Nanoparticles at the Gas/Water Interface: An X-ray Scattering Study", J. Chem. Phys. 120, 3446 (2004).
- M. Fukuto, R.K. Heilmann, P.S. Pershan, S.M. Yu, C.M. Soto, and D.A. Tirrell, "Internal Segregation and Side Chain Ordering in Hairy-Rod Polypeptide Monolayers at the Gas/Water Interface: An X-ray Scattering Study", J. Chem. Phys. 119, 6253 (2003).
- M. Fukuto, R.K. Heilmann, P.S. Pershan, S.M. Yu, C.M. Soto, and D.A. Tirrell, "Confinement Induced Order of Tethered Alkyl Chains at the Water/Vapor Interface", Phys. Rev. E 66, 010601(R) (2002).
- M. Fukuto, R.K. Heilmann, P.S. Pershan, S.M. Yu, J.A. Griffiths, and D.A. Tirrell, "Structure of poly(g-benzyl-L-glutamate) monolayers at the gas/water interface: A Brewster angle microscopy and x-ray scattering study", J. Chem. Phys. 111, 9761 (1999).
Abstract
- M. Fukuto, R.K. Heilmann, P.S. Pershan, J.A. Griffiths, S.M. Yu, and D.A. Tirrell, "X-Ray Measurements of Noncapillary Spatial Fluctuations from a Liquid Surface", Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 3455 (1998).
Abstract
- M. Fukuto, K. Penanen, R.K. Heilmann, P.S. Pershan, and D. Vaknin, "C60-propylamine adduct monolayers at the gas/water interface: A Brewster angle microscopy and x-ray scattering study", J. Chem. Phys. 107, 5531 (1997).
Abstract
- G.M. Bommarito, W.J. Foster, P.S. Pershan and M.L.
Schlossman, "A determination of the phase diagram of relaxed Langmuir
monolayers of behenic acid", J. Chem. Phys.
105, 5265 (1996).
- W.J. Foster, M.C. Shih and P.S. Pershan, "The
structure of a langmuir monolayer of methyl eicosanoate as determined by
x-ray diffraction and Brewster-angle microscopy", J. Chem. Phys. 105, 3307 (1996).
- W.J. Foster, M.C. Shih and P.S. Pershan, "The
structure and phases of a relaxed Langmuir monolayer of methyl eicosanoate
as determined by grazing incidence x-ray diffraction and Brewster angle
microscopy", Materials Research Society,
Symposium AA: Applications of Synchrotron Radiation Techniques to Materials
Science II 375, 187 (1995).
- D.K. Schwartz, M.L. Schlossman and P.S. Pershan,
"Re-entrant appearance of phases in a relaxed monolayer of
tetraconsanoic acid as determined by x-ray scattering", J. Chem. Phys. 96, 2356 (1992).
- M.L. Schlossman, D.K. Schwartz, E.H. Kawamoto, G.J.
Kellogg, P.S. Pershan, M.W. Kim and T.C. Chung, "X-ray Reflectivity of
a Polymer Monolayer at the Water/Vapor Interface", J. Phys. Chem. 95, 6628 (1991).
- M.L. Schlossman, D.K. Schwartz, P.S. Pershan, E. H.
Kawamoto, G.J. Kellogg and S. Lee, "Relaxation and Appearance of a
Reentrant Phase in a Molecular Monolayer", Phys. Rev. Lett. 66, 1599 (1991).
- M.L. Schlossman, D.K. Schwartz, E.H. Kawamoto, G.J.
Kellogg, P.S. Pershan, B.M. Ocko, M.W. Kim and T.C. Chung, "X-ray
studies of the liquid/vapor interface: water and polymer and fatty acid
monolayers on water", Mat. Res. Soc. Symp.
Proc. 177, 351 (1990).
- D.K. Schwartz, M.L. Schlossman, E.H. Kawamoto, G.J.
Kellogg, P.S. Pershan and B.M. Ocko, "Thermal diffuse scattering
studies of the water-vapor interface", Phys.
Rev. A 41, 5687 (1990).
- D.K. Schwartz, A. Braslau, B.M. Ocko, P.S. Pershan, J.
Als-Nielsen and J.S. Huang, "X-ray reflectivity studies of a
microemulsion surface", Phys. Rev. A 38,
5817 (1988).



